Virtualizing iOS on Apple Silicon
In this blog post, I explore how I achieved virtualizing iOS on Apple silicon Macs, exploring many internals along the way.
Part 0: Uncharted Waters?
One large project I’ve spent large amounts of time working on was vma2pwn, a project that can create a fully modifiable vma2 macOS boot-chain for macOS guest virtual machines. This was actually a preliminary project to this one—in other words, figuring out how to walk before learning how to run. With recent developments such as the Mac transition to Apple silicon and Mac Catalyst, the iOS and macOS operating systems were brought much closer together than they ever have been before; with the introduction of macOS virtualization on Apple silicon Macs, this begged the question: could iOS (and the macOS boot-chain) be modified in such a way to virtualize it as well?
iOS on macOS? These are rather uncharted waters. vma2ios exists, but has not been (intentionally) publicized. Additionally, the macOS version of XNU and iBoot differs enough to require difficult modifications that result in only a partially-working solution.
Relevant Prior Research
I am not the first to embark on the topic on iOS virtualization/emulation. Here are some notable projects and companies that have approached this subject already that you may be interested in reading up on:
- Corellium and their virtual iPhone cloud product (only publicly-available “complete” solution)
- qemu-t8030
- Helpful tools, code, and applicable modifications to iOS which proved insightful
- Other QEMU
- Zhuowei Zhang’s blog
- Outside of their previous blog posts on emulating iOS on QEMU, this article also proved briefly
helpful when I learned about the relationship between macOS’s
IOSurfaceRootand iOS’sIOCoreSurfaceRootwhen exploring necessary kernel patches. Zhuowei concluded that (GUI) macOS applications cannot run on iOS—but (graphical) iOS apps can run on macOS. Mac Catalyst seems to work, expectedly, only one way. Luckily, this holds true not just for iOS apps, but the majority of iOS’s graphical systems.
- Outside of their previous blog posts on emulating iOS on QEMU, this article also proved briefly
helpful when I learned about the relationship between macOS’s
- Others
Part I: Getting Started + a New Discovery
As I was drafting this (overdue) article, I discovered a useful-yet-infuriating feature in Apple’s Virtualization stack—the ability to sign arbitrary data for the virtual machine. As mentioned, I created the vma2pwn project for the purpose of patching the vma2 stack to allow for a chain of modified firmware; however, this proved to be largely pointless.
Apple’s Virtualization.framework has an undocumented private function:
_setProductionModeEnabled(false). This useful call (and it’s VM configuration equivalent) demotes
the VM to a Chip Fuse Mode (CPFM) of 01, which configures the virtual device as “secure” and
“non-production.” With physical hardware devices, Apple’s Tatsu Signing Server (TSS), reponsible
for providing SHSH blobs required for firmware installation, refuses to sign firmware for any
non-production/non-secure device (CPFM of 00 or 01). However, TSS does sign firmware for
the public vma2 device—any firmware provided, in fact! Now I don’t have to feel bad about only
supporting 12.0.1 in vma2pwn…
Now, to get started, a strategy for approaching the daunting task of running iOS on vma2 is needed.
I found the most success with reusing a fully macOS 12.0.1 bootchain and simply replacing the
system (OS) image, along with its associated mtree, root_hash, and trustcache files, with
that of the iOS 15.0.2’s (iPhone XR build). This would largely bypass the need for (almost) any
modifications before iOS initializes, such as to the bootchain and ramdisk (restore process). The
XR build was chosen for its arm64e capability and lower-resolution (if that mattered). You should
see success with other arm64e device configurations, but do note that the vma2 kernel is hardcoded
to return "iPad8,6" for some sysctl key. arm64 versions experienced additional issues and binary
incompatibilities, so there is no point in trying these builds.
I used my own fork of tart (a third-party application for managing Apple silicon virtual machines),
super-tart for running the iOS VM, which allows
for using the required undocumented features provided by Virtualization.framework. I have not yet
pushed all of my changes, such as for setting _setProductionModeEnabled(false). Do note that such
Virtualization.framework tools that use private APIs require SIP to be turned off, and maybe AMFI
as well. I also use
my own fork of idevicerestore.
Part II: Patch Purgatory
Welcome to Patch Purgatory, where you pay with time and leave with regret. This section attempts to review the patches I made to get to the point of booting iOS enough, as shown in the demo at the end. These are not necessarily in chronological order.
Kernel Patches
The first patches one needs are potentially the ones I did for vma2pwn, but I am not sure if any
are necessarily needed if using the CPFM 01 trick detailed above. These include patches to
_apfs_extract_root_hash_arm, _authenticate_root_hash, __img4_firmware_property_callback,
_is_root_hash_authentication_required, and _img4_firmware_evaluate to return 0 in the vma2
kernel. Additionally, lookup_in_static_trust_cache needs to be patched to return 1. These are
your run-of-the-mill signature patches and won’t be further detailed.
So, with our sigcheck-patched kernel, we try to boot iOS from a fresh restore and run into an
expected problem: our executables are terminated with EXEC, [0xe] Binary with wrong platform,
since these are not simulator platform binaries! This is an easy fix, patching this line in
XNU
to skip the PLATFORM_IOS check. This can be done in the vma2 kernel by patching the B.NE to B
as shown here:
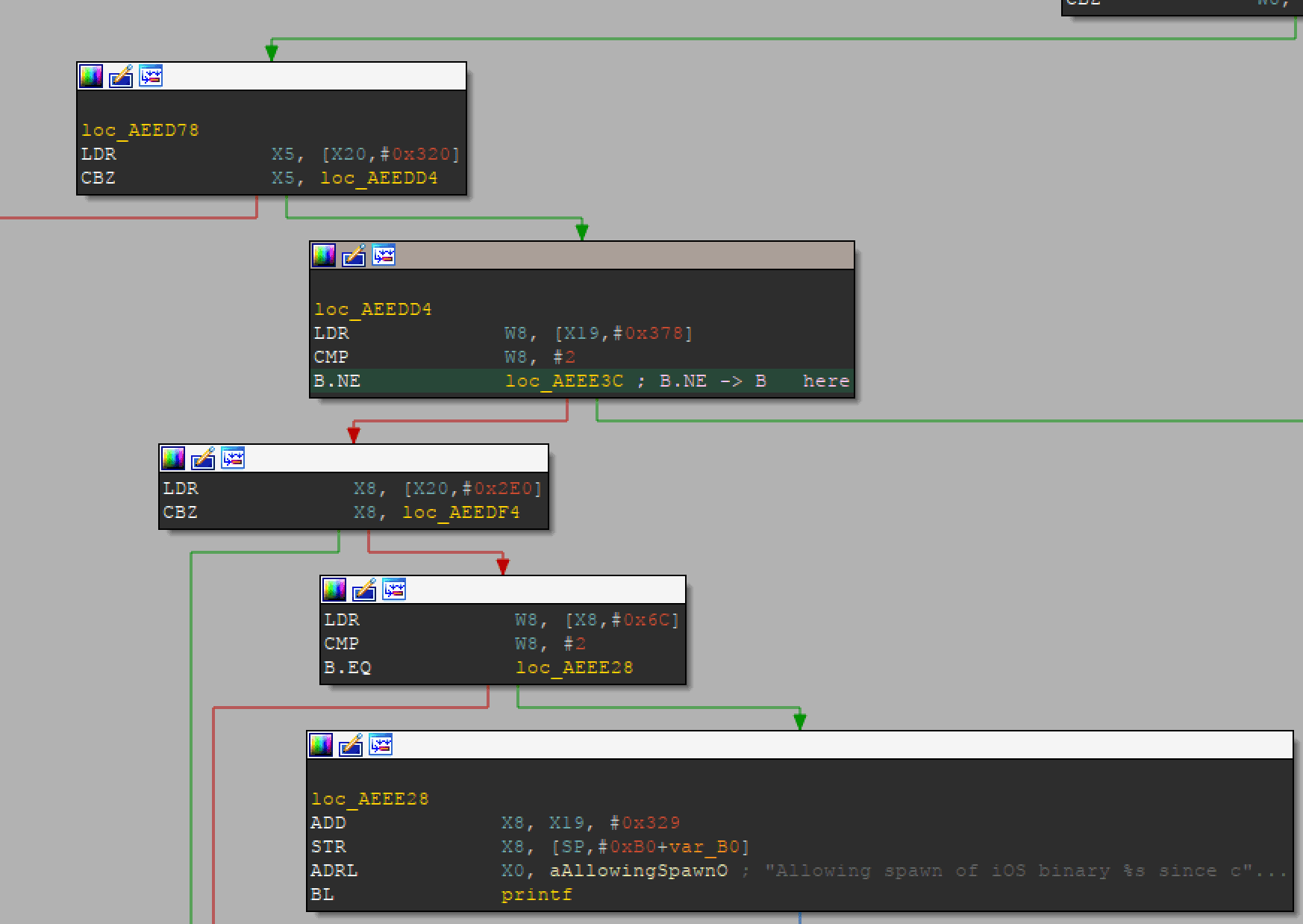
Now our modded kernel will launch iOS binaries without issue.
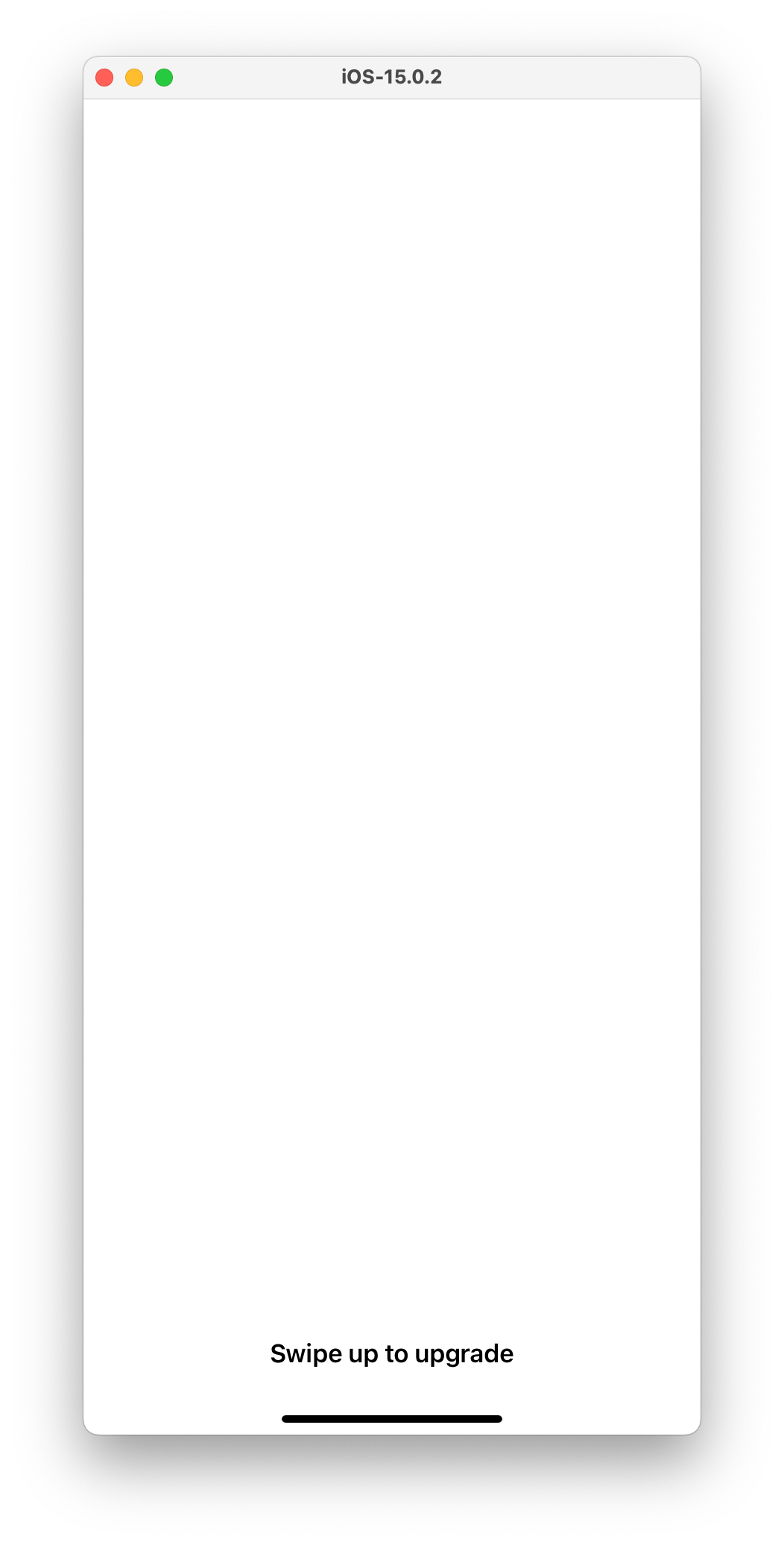
An issue one might encounter is related to the system keybag, of which there are incompatibilities
down the rabbit hole—this is Patch Purgatory, after all. This is what causes PreBoard.app to ask
the user to “Swipe up to upgrade.” instead of showing Setup.app (normal setup); the iOS system and
macOS kernel just aren’t very compatible in regards to keybags, unfortunately. I have yet to
overcome this limitation, other than making two patches to ipc_make_system_keybag to force the
function to not return an error, which at least gets us to PreBoard.app.
Another kernel issue I encountered is the size mismatch between the IOMFB struct passed between
iOS system frameworks and the macOS kernel. This causes a kernel panic with the string
CLCDTransaction size mismatch. Returning error 0x%X.. I thought this was going to be a dead-end,
but to my surprise, patching out the size check in IOMobileFramebufferUserClient::swap_submit
stopped it from panicking! This concludes the kernel patches.
System Patches Preface
In the following section, I detail the patches needed for non-kernel components in the restore
ramdisk (a ramdisk sent by the host to the virtual device that is essentially a stripped-down iOS
that is used to carry out the restore process), as well as iOS system files. These files are
signed, and will be killed if ran if patching them without re-signing. In our modified environment,
I suggest using Procursus’s ldid (brew install ldid-procursus) and re-signing with
ldid_macosx_arm64 -S -M <binary>; the -S parameter pseudo-signs the binary, and the -M
parameter preserves the existing entitlements in this context. Note that many binaries have an
identity that is checked and will need to be renamed before being re-signed, then renamed back. For
example, to re-sign keybagd, one needs to find the proper Identity with codesign -d -v keybagd,
which tells us Identifier=com.apple.keybagd, and rename it to this identity
(mv keybagd com.apple.keybagd), then re-signing with ldid
(ldid_macosx_arm64 -S -M com.apple.keybagd), and finally renaming it back
(mv com.apple.keybagd keybagd).
Additionally, to find the named functions to patch if they are not symbolicated automatically, search for the string XRef using your disassembler of choice and trace the caller function via the logging call reference.
You may also want to port over Bash and add a LaunchDaemon in order to get an interactable shell through the serial terminal. This can be done by simply copying the relevant files from a version-compatible iOS jailbreak payload such as with Procursus.
System Patches
In order to patch the system (or the restore ramdisk), one needs to directly modify the DMG volume.
This can be done first by converting the iOS System volume (included in the desired version’s IPSW)
to a read-and-writable version with, for iOS 15.0.2, for example,
hdiutil convert -format UDRW -o 018-66258-074-rw.dmg 018-66258-074.dmg (if I remember correctly).
Now, once it is first initially mounted (e.g., by double-clicking on it), mount it as properly
writable again with, for example, sudo mount -uw /Volumes/Sky19A404.N104N841OS. Now, while using
sudo through the Terminal, update the files as desired (like the ones modified as follows). Once
finished, this R/W DMG can be converted back to a usable version for your restore tool by first
running hdiutil convert -format ULFO -o 018-66258-074.dmg 018-66258-074-rw.dmg, and then running
asr imagescan --source 018-66258-074.dmg. You may want to keep the R/W version around for
quick-turnaround modification.
Before iOS boots, the restore ramdisk needs a little fixing up—specifically,
/usr/local/bin/restored_external. This is due to the fact that the iOS version of
restored_external attempts to create the system keybag with MKBKeyBagCreateSystem, but this is
not compatible with our macOS kernel, so the error check can easily be patched out. Another patch
needed is to skip root hash authentication, by patching the conditional that calls the
ramrod_set_NVRAM_variable function to set allow-root-hash-mismatch to true (1).
Another ramdisk modification needed is to /usr/sbin/asr. One should be able to easily patch this
with iSuns9’s version of asr64_patcher. Specifically,
one needs to find the function that prints the string "Image failed signature verification.",
then find the function which references this function, then patch the BL ARMv8-A call there with
a B jump down to where the string "Image passed signature verification" is referenced (placed
in X0 before calling _warnx). In the asr binary from 15.0.2, this would be patched with
b #0x7c at file offset 0x27A18.
Now, the iOS system itself needs fixing up to become compatible with the macOS kernel. The main
change is to move most files stored on the system volume that will be installed in the root of the
filesystem into /System/Library/Templates/Data. These will be present in / once the system
boots. Do note that empty folders in the normal root in the system volume may still need to exist,
even though empty (e.g., /Applications), though I have not done enough testing surrounding this.
Very early in the iOS boot process, /sbin/launchd runs to initialize early boot processes.
Patches are needed to allow it to run without failing. The first patches are to the embedded
configuration plist, which can be found in the binary by searching for the string
<key>SIGTERMTimeout</key> and looking back about 172 bytes. The first of these patches which may
be required is adding <key>PerformAfterUserspaceReboot</key><true/> to the embedded configuration
plist sections mount-phase-2, fips, tzinit, finish-demo-restore, fud, xpcroleaccountd,
prng_seedctl, and MSUEarlyBootTask in order to get closer to the macOS version of launchd
functionality. Additionally, in the data-protection section, RequireSuccess can be changed to
<false/>. This is needed due to the iOS version of /usr/libexec/init_data_protection (symlinked
to /usr/libexec/seputil) failing due to running in a virtual machine. These modifications to the
embedded configuration plist will likely not fit under the existing size of the string; luckily,
one can easily work around this by using an XML minimizer and pasting this minimized XML over the
old one, then overwriting the rest of the string with some XML-friendly whitespace (e.g., hex
0x20 for space characters).
A keybagd Aside
Another responsibility of launchd is to initialize /usr/libexec/keybagd; this binary will fail
due to the aforementioned kernel differences. This problem can be hacked around in various ways;
one way is by compiling a simple executable to simply exit with a return code of 0 to replace
keybagd with. I explored the possibility of resolving these system keybag differences; the
fixkeybag project by NyanSatan was a point of interest
for this. However, the code to generate a system keybag in this application designed for enabling
iOS dual-boots simply calls MKBKeyBagCreateSystem, just like the failing code in the restore
ramdisk binary restored_external. This would still fail in the booted iOS state, as well.
One additional patch to launchd is needed; a NOP patch to the conditional branch (TBZ) that
results in the error Userspace reboot changed system version: previous %s != current %s being
printed as a panic string.
After launchd, we quickly run into an expected issue, related to the disk volumes. Because we are
using a macOS bootchain, including a macOS ramdisk for the restore process, the /sbin/mount
binary on iOS has no idea how to manage the APFS volumes created. Fortunately, this is once again
an easy fix: simply replace the binary with the one from the macOS system volume after modifying
its Mach-O metadata to run on iOS. I did this manually, but you can use vtool which is included
in macOS, as well.
Now, a difficult modification is needed—a patch to the DYLD shared cache. Like the previously
mentioned, IOSurfaceRoot in macOS and IOCoreSurfaceRoot on iOS are basically the same driver,
but are incompatible with their different names. Luckily, because the DYLD shared cache (DSC) for
iOS uses the longer of the two strings, it is trivial to patch it to match the macOS’s vma2 kernel
driver name from "IOCoreSurfaceRoot" to "IOSurfaceRoot", filling in the rest of the remnants of
the old string with zeroes (0x00). In order to do this, I suggest installing the ipsw tool
created by blacktop. Using this, one can extract the embedded
dylibs for easy modification (good luck analyzing a full DSC in IDA!) with
ipsw dyld split <dsc file>. Then, you can find the
/System/Library/Frameworks/IOSurface.framework/IOSurface binary that requires these modifications
(without telling you, you should find an error pointing here anyway). The virtual addresses should
be preserved if you use a decent DSC extractor and disassembler combo; then, it is trivial to find
the reference to the string "IOCoreSurfaceRoot", in the __iosConnectInitalize function. If you
are curious, you can see that it calls an unknown function at the address 0x1A38D5F58; some
functions of ipsw error out in my experience, but ipsw dyld dump always works. Using this
command, one can see it pointing to some data in
/System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/ktrace.framework/ktrace. When disassembling this binary at the
same address, one can see that it is, unsurprisingly, the function IOServiceNameMatching; this
isn’t actually important, however. Moving on, you can use the ipsw dyld a2o command to convert
the original virtual address (of the modified string "IOSurfaceRoot") into the file offset to
patch the DYLD shared cache file itself (in this case, 0x28fde373 in dyld_shared_cache_arm64e).
After this modification, there is some cdhash thing in another part of the DSC that will no longer
be valid, which will produce an exception when you restore this modified system. I don’t understand
it much, but I found that one way to get through this issue is to set a breakpoint in the kernel
(can be done through the GDB stub provided by a Virtualization.framework frontend like super-tart)
in the cs_validate_hash function, specifically at the end of the function that contains the
string "CODE SIGNING: cs_validate_page: mobj %p off 0x%llx size 0x%lx: actual [0x%x 0x%x 0x%x 0x%x
0x%x] != expected [0x%x 0x%x 0x%x 0x%x 0x%x]\n". Unfortunately, despite the proper boot-args, this
printf call only prints a truncated version (also with flipped endianness) of the new and old
cdhashes, so this breakpoint is needed to find the complete cdhashes. You can then look at the
entire old cdhash and search for it using a hex editor in the DSC. In this case, for 15.0.2, it can
be found at the file offset 0x5a9cffc0, and the bytes
16D6BA49 065E212B ECC422B4 C0965F3B 2D8B70CA 48E0EE18 11E50A10 807D1BD5 should be patched to the
new cdhash (depending on the exact patch you made), which should be
A44E9EEA 2A6185E0 E3E5FB90 5F51055A FBF55912 2081A217 039AF2DB D09FC715 if you followed my patch
instructions exactly. Now, iOS should have no problems with our modified DSC.
One harmless crash we come across is watchdogd; this crashes because it lacks the code path that
exists in the macOS version that checks if it is running in a VM, then gracefully exits. This just
means that watchdogd will crash-loop. Disregard.
In backboardd, I experimented with patching calls that may trigger PreBoard.app, such as data
migration. I didn’t realize any difference with this other than getting stuck on the Apple logo.
In lockdownd, specifically in the get_device_type_internal_block_invoke function (can be found
by the log string xref), the getMGInt call (ditto) for "ShouldHactivate" should be patched with
mov x0, #1 to force lockdownd to “hactivate” (bypass normal iOS activation restrictions in
development environments).
Like previously, mobileactivationd can be patched to allow for hactivation, as well. The
shouldHactivate function should be patched with the ARMv8-A instructions mov x0, #0 and then
ret.
Any additional modifications that may be needed to the vma2 device tree is left as an exercise to the reader. 🙂
This sums up most, but probably not all of the specific modifications needed to get a similar setup
up and running. You may need to do weird things like chmod -R 777 / to try and get some things
working.
Part III: The Future
Getting past the system keybag issues requires many more patches and an understanding of the system
as it exists in the iOS system and kernel that I currently lack. This project has already taken at
least a few hundred hours of exploration, and I’d be curious to see if anyone can take it further
than just booting to PreBoard.app.
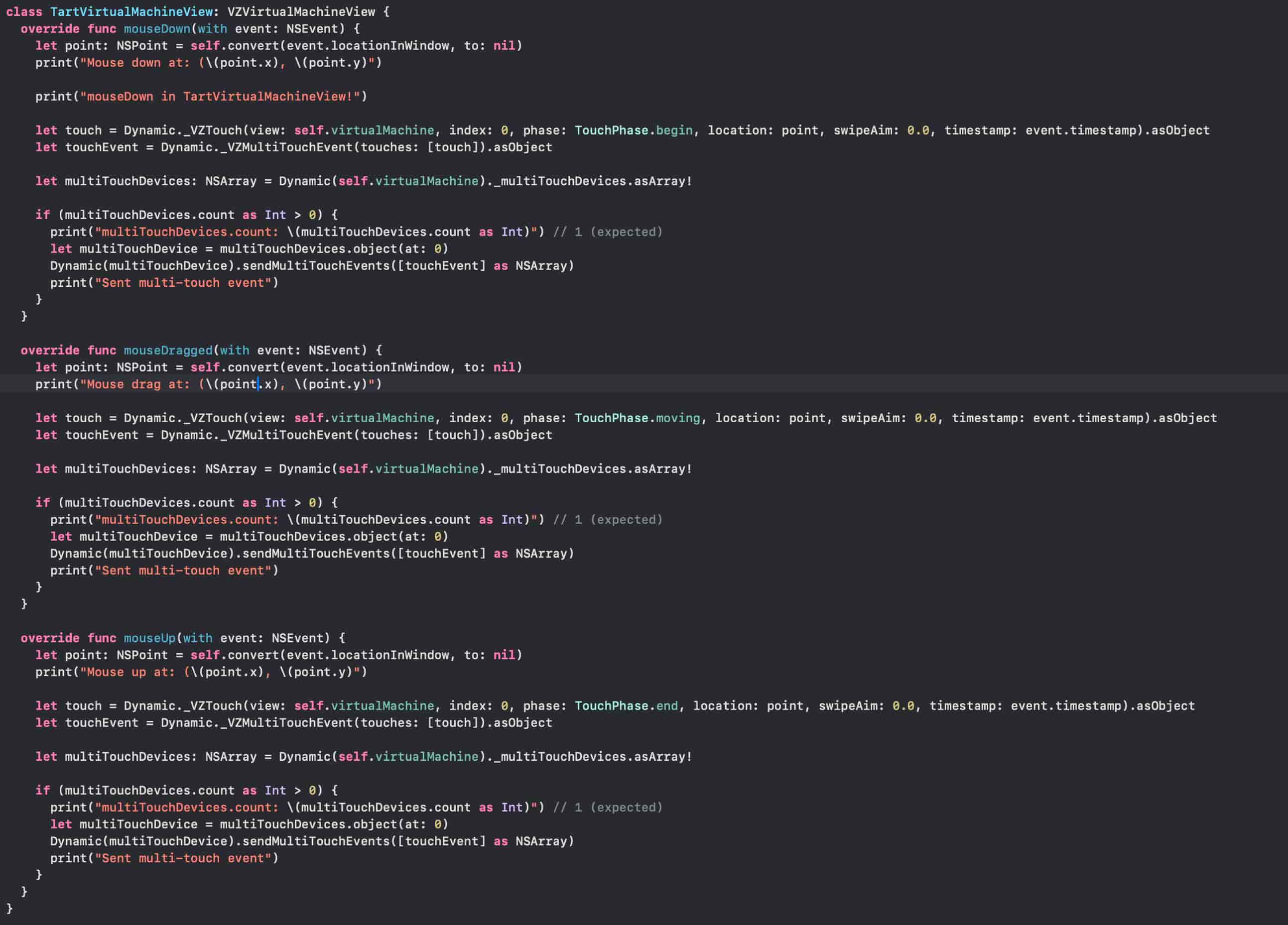
I have also not yet discovered if touch functionality is functional through the public vma2 Mac
kernel and firmware. However, in the case that it does, Virtualization.framework provides
undocumented API functions for this, such as the _VZAppleTouchScreenConfiguration and
_VZUSBTouchScreenConfiguration devices. These can then be used with the _VZTouch and
_VZMultiTouchEvent objects to send touches. I have not fully figured out the exact parameter
usage, but some example code that should be fairly close to the correct implementation can be
found below. Note the TouchPhase enum which is just a simple enum that implements the same
named values as NSTouch.Phase. This may sometimes generate an exception, and I have no idea
if the coordinate values are mapped correctly to what the VM expects, if it can even handle it.
See the example implementation below.
If anyone would like further guidance or access to the numerous files involved with this project (my setup is a bit unsightly), please do not hesitate to contact me!
Demo
For the final conclusion of this blog post, enjoy this video demo (with a half-minute waiting period clipped out) showing off the boot sequence.
* By playing the video, you are agreeing to YouTube’s Terms of Service.